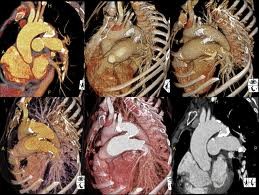
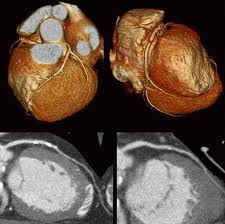
Coronary
CTA
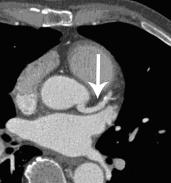
Coronary CTA is reliable and non-invasive assessment of stenosis in the proximal and mid regions of the coronary arteries, where the majority of stenosis are found. Both the sensitivity and specificity for the detection of clinically significant stenosis are about 90%. Coronary CTA can image blood vessel walls and the anatomy of the heart. In addition, both calcified and non-calcified atherosclerotic plaques can be seen in coronary CTA images and, therefore, it is possible to assess a patient’s total calcified and non-calcified plaque burden.
Indications for Coronary CTA
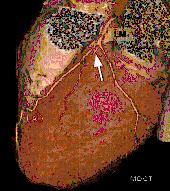
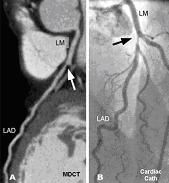
Patients who
are most
likely to benefit from coronary CTA are those who
have atypical symptoms and are of intermediate risk for coronary artery
disease. Other indications for coronary CTA may include patient refusal
of conventional cardiac catheterization and detection/quantification of
cardiac calcification.
Patient Preparation
In order for coronary CTA imaging to be successful, the heart rate must be less than 65. Therefore, if a patient’s heart rate is more than 70, he or she must take a ß-blocker the evening before and the morning of the scan. If the heart rate is too high immediately before the scan, intravenous ß-blockers may be administered. No food or drinks should be consumed in the last 4 hours before the scan. As a precaution when using contrast agents, all patients must have a recent measure of their serum creatinine level. Patients may take their regular medication, with the exception of metformin (Glucophage), which should be discontinued for at least 48 hours after the scan.
Radiology report will be available within 48-72 hours.
Click here to see a sample of a CTA report from Ocean Radiology in Brooklyn.
Coronary CTA is reliable and non-invasive assessment of stenosis in the proximal and mid regions of the coronary arteries, where the majority of stenosis are found. Both the sensitivity and specificity for the detection of clinically significant stenosis are about 90%. Coronary CTA can image blood vessel walls and the anatomy of the heart. In addition, both calcified and non-calcified atherosclerotic plaques can be seen in coronary CTA images and, therefore, it is possible to assess a patient’s total calcified and non-calcified plaque burden.
Indications for Coronary CTA
Patient Preparation
In order for coronary CTA imaging to be successful, the heart rate must be less than 65. Therefore, if a patient’s heart rate is more than 70, he or she must take a ß-blocker the evening before and the morning of the scan. If the heart rate is too high immediately before the scan, intravenous ß-blockers may be administered. No food or drinks should be consumed in the last 4 hours before the scan. As a precaution when using contrast agents, all patients must have a recent measure of their serum creatinine level. Patients may take their regular medication, with the exception of metformin (Glucophage), which should be discontinued for at least 48 hours after the scan.
Radiology report will be available within 48-72 hours.
Click here to see a sample of a CTA report from Ocean Radiology in Brooklyn.